Results
A network representation for PID classification. The image contains links to fact files for diseases in the ImmunoDeficiency Resource.
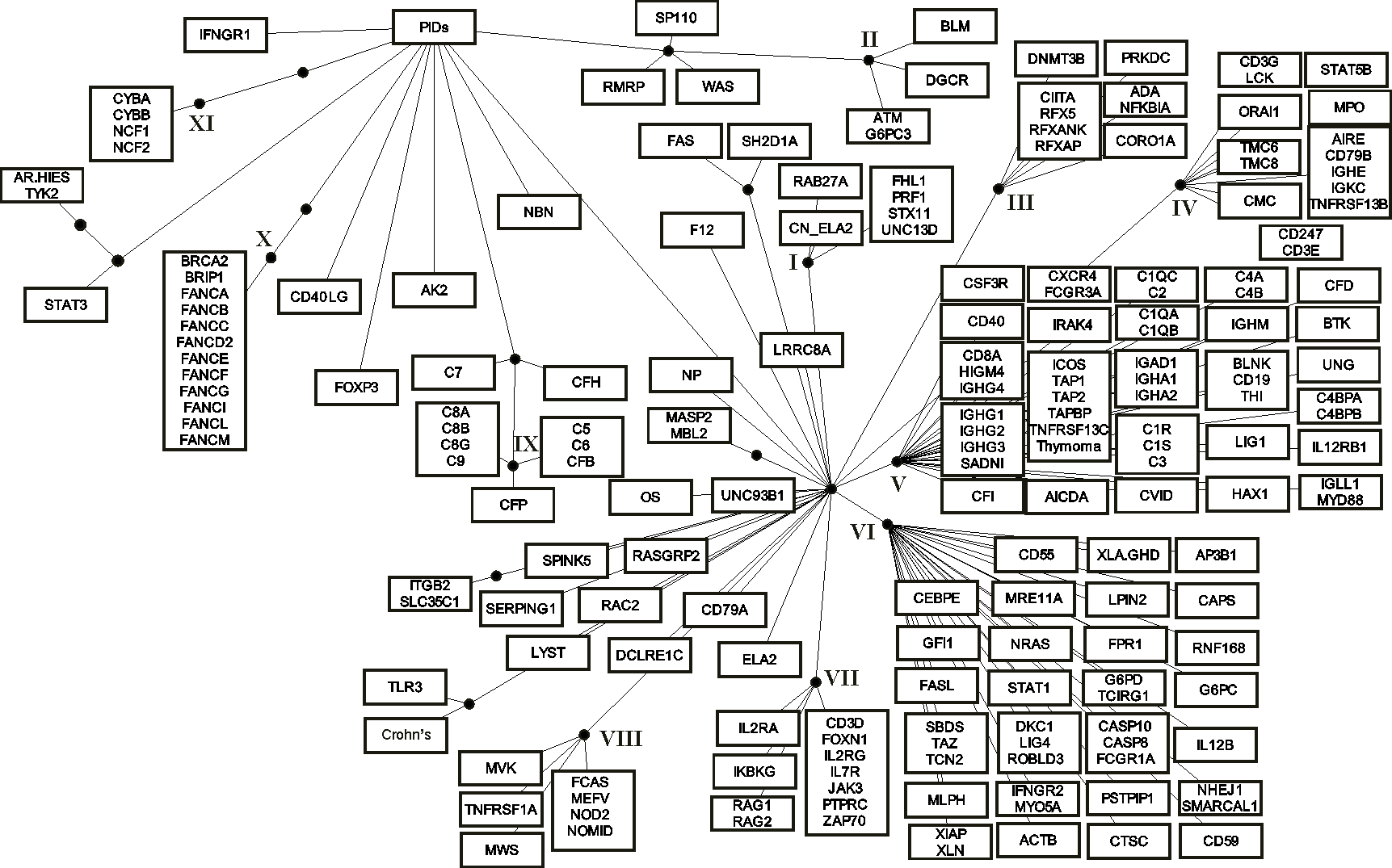

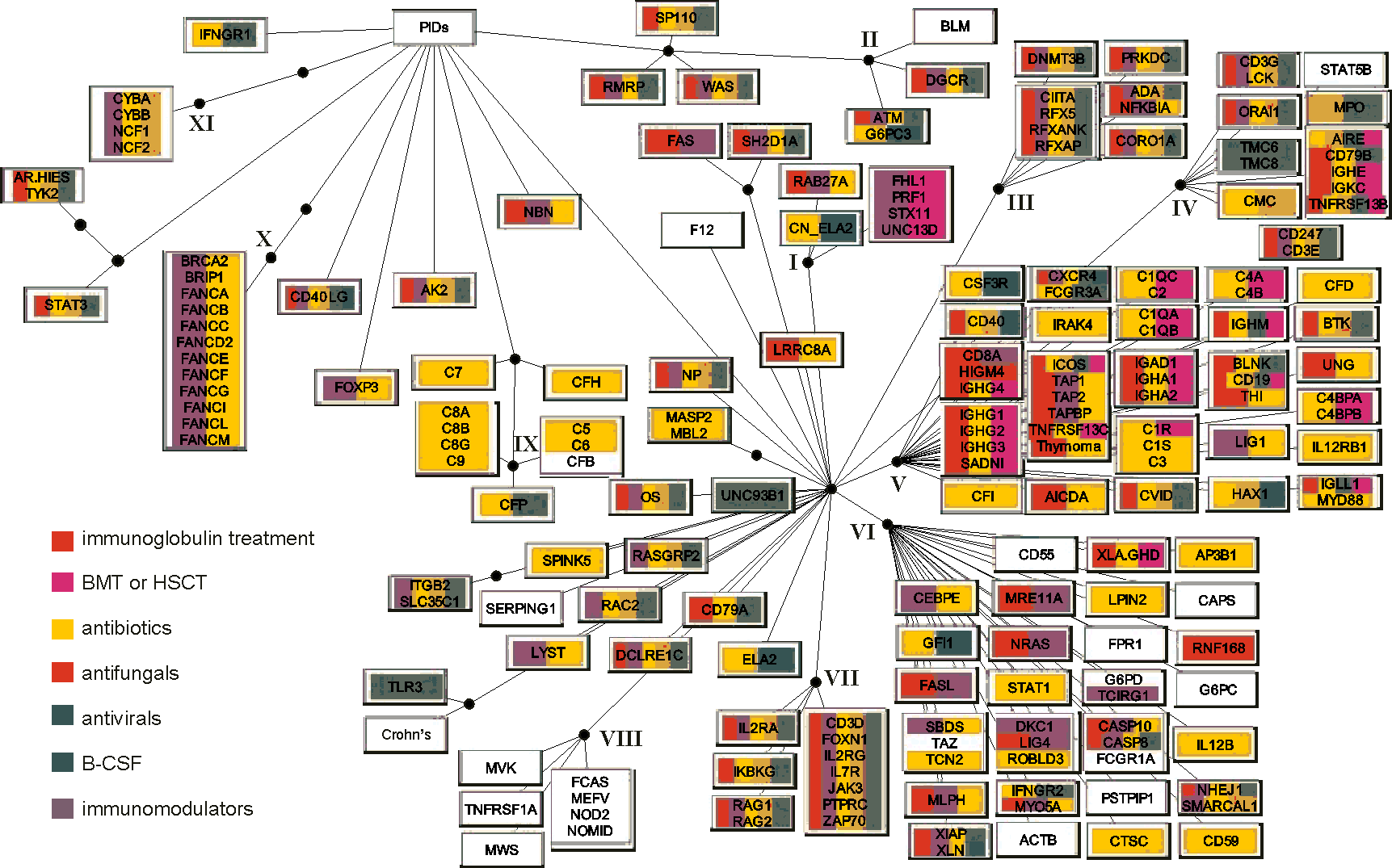
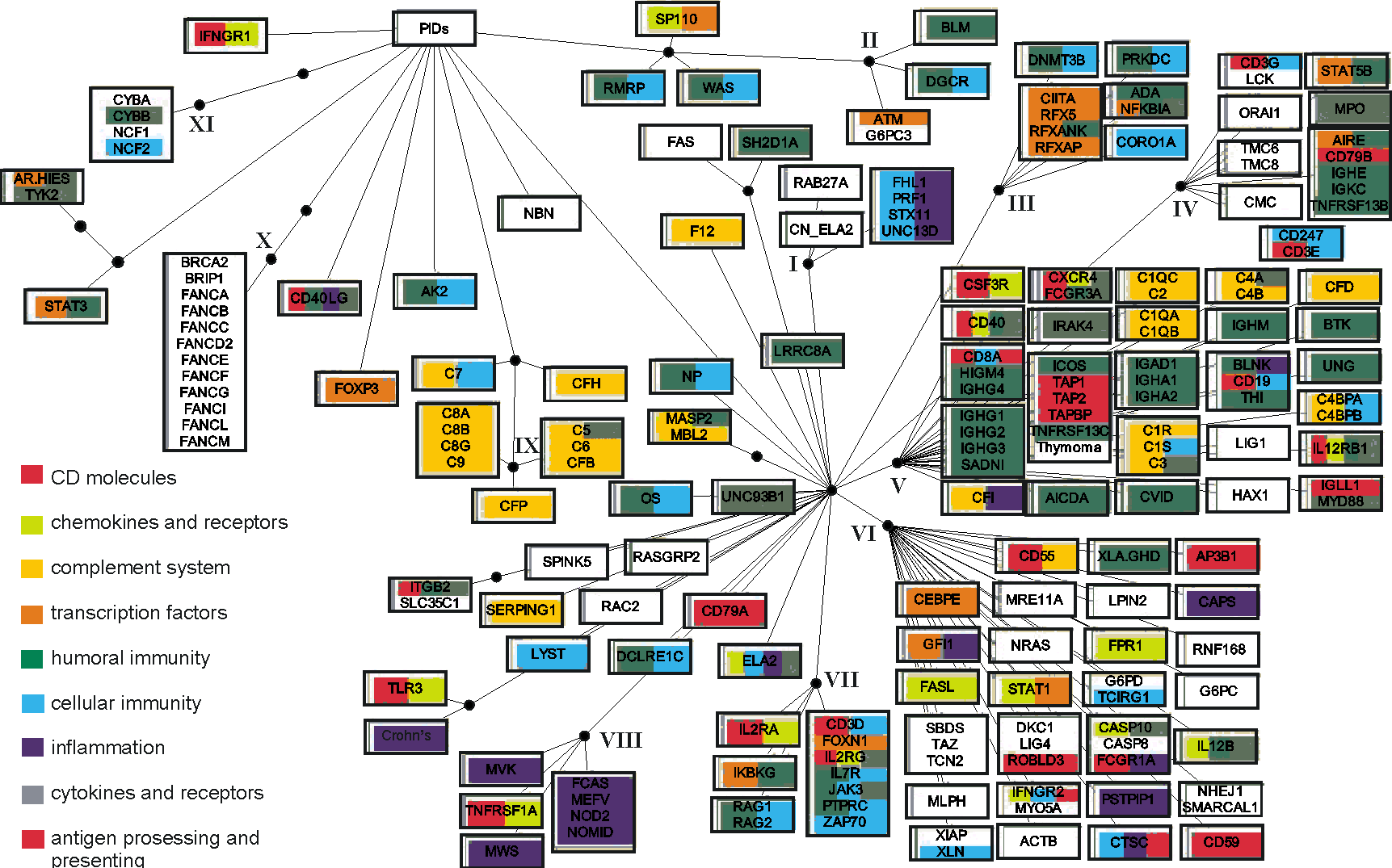
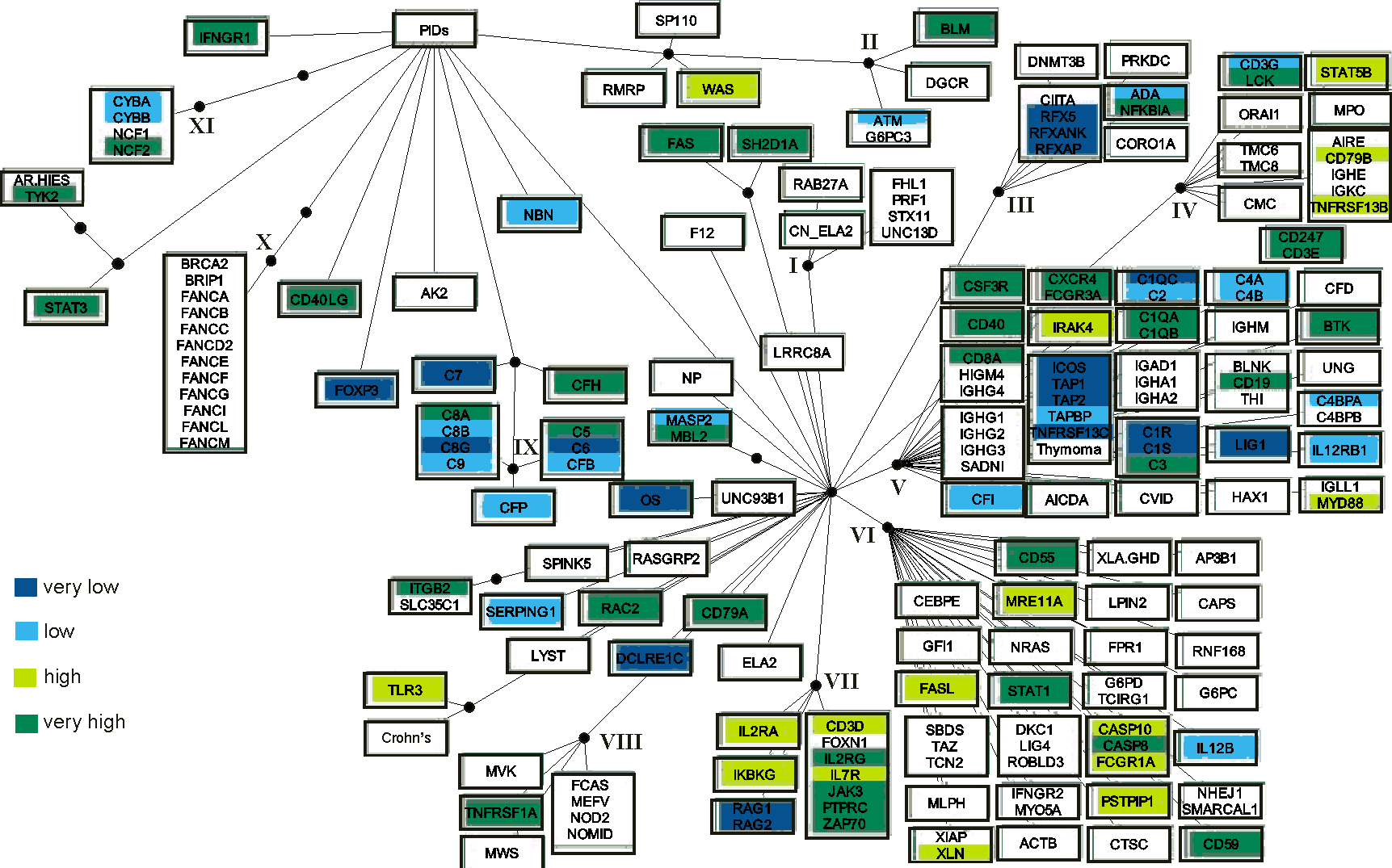
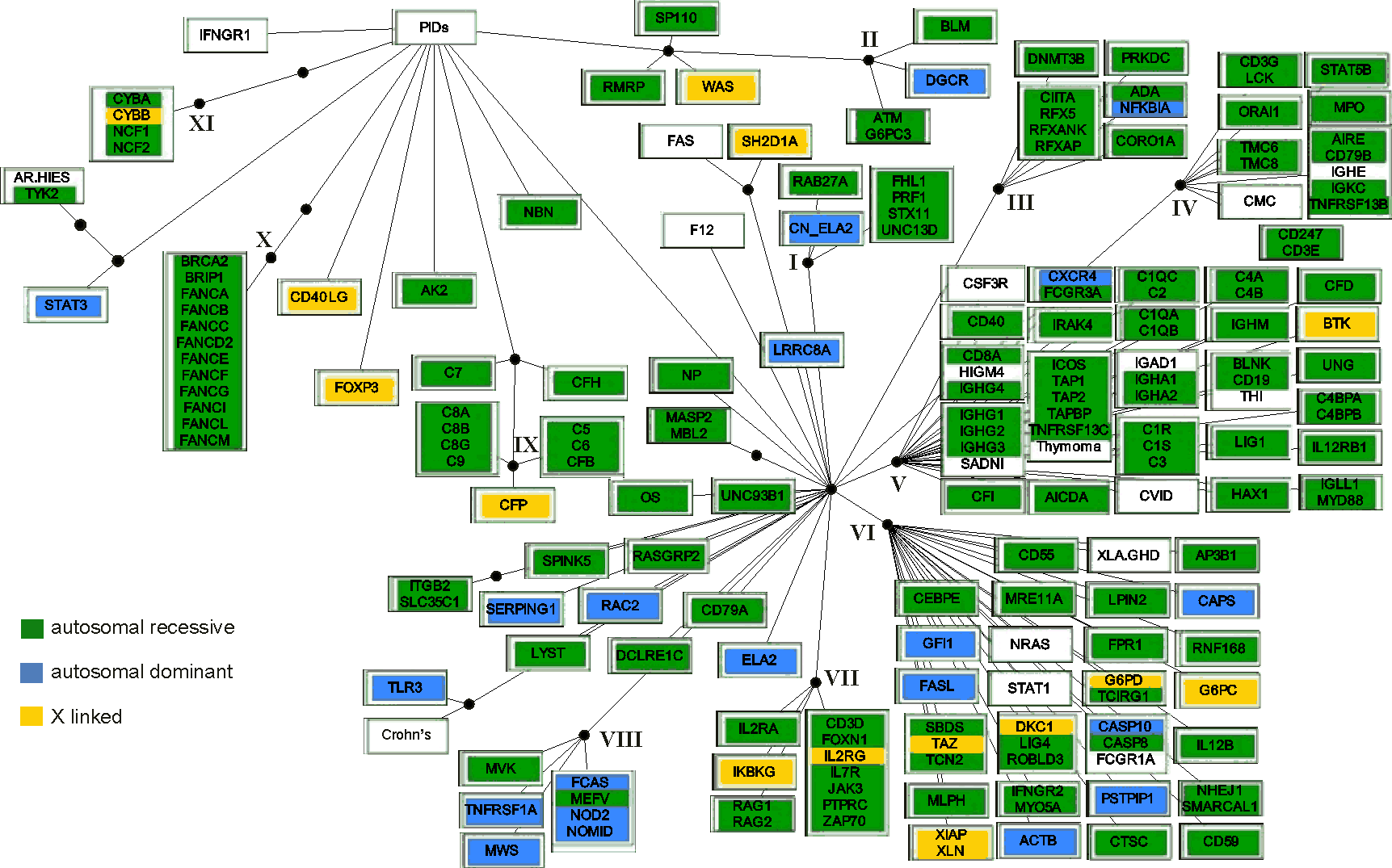
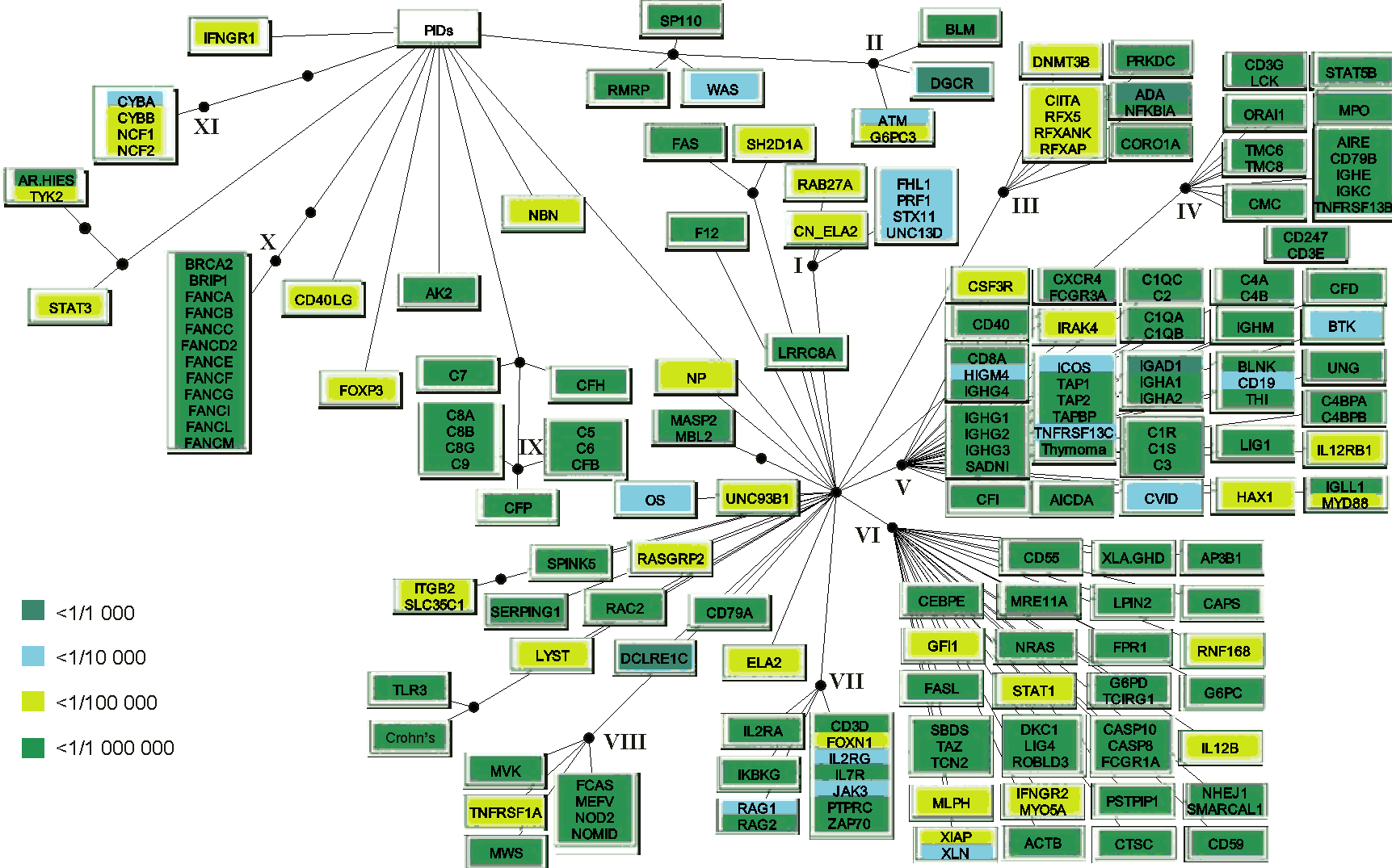
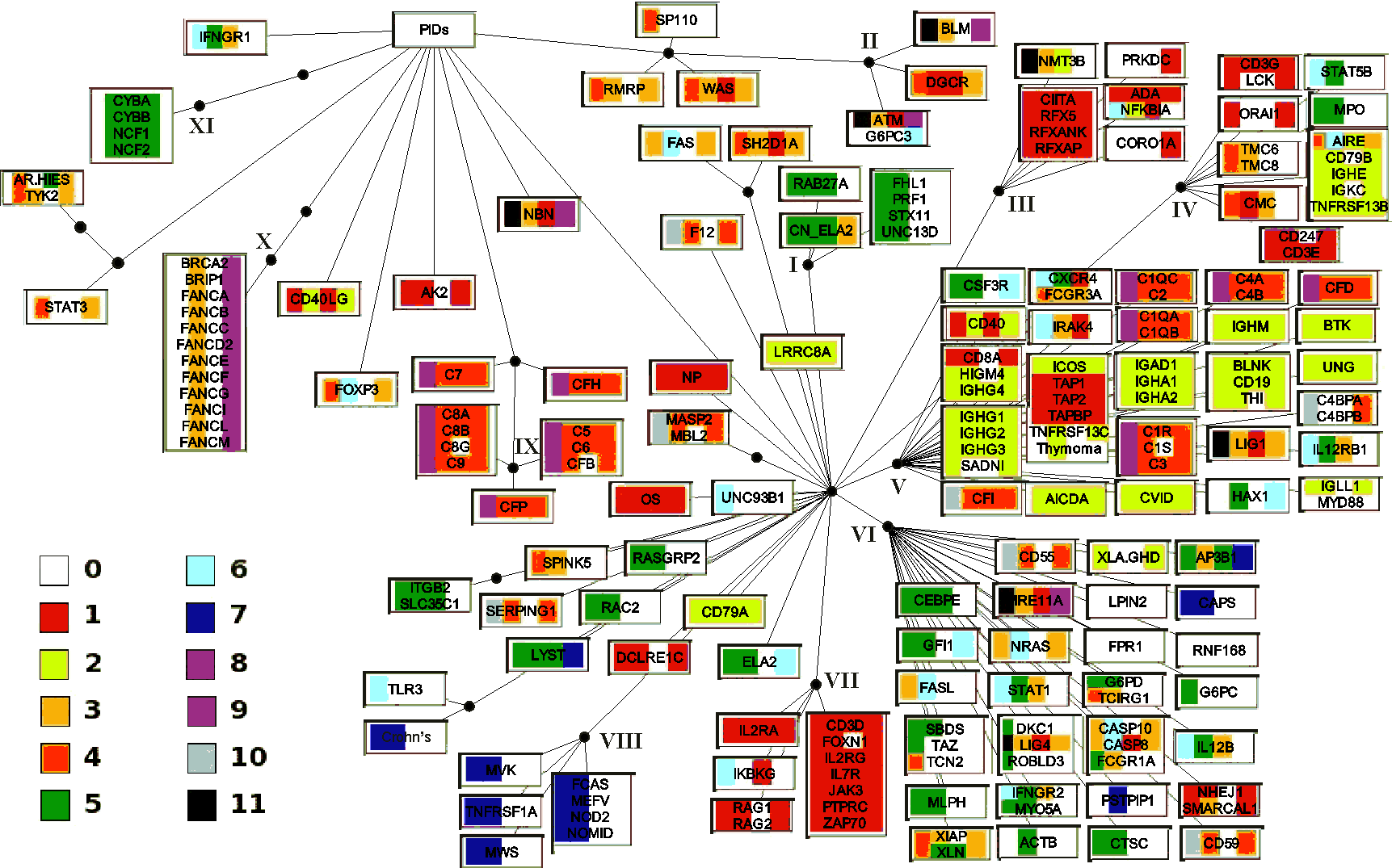
Consensus for the six methods used to group the PIDs. The white rectangles indicate the grouping of diseases by five (those attached to the first black bullet from the PIDs root) and six (the second bullet) methods. Diseases are indicated by the systematic names of affected genes, when known. Otherwise, the following names were used when no genes are identified in relation to the disease: AR-HIES, autosomal recessive hyperimmunoglobulin E recurrent infection syndrome; CMC, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis; CVID, common variable immunodeficiency; FHL1, familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 1; HIGM4, hyper-IgM syndrome type 4; SADNI, specific antibody with normal Ig level or hyper Ig; THI, transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy; Thymoma; XLA/GHD, X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia with growth hormone deficiency. When one gene is involved in more than one disease the following abbreviations were used: CAPS, cryopyrin associated periodic syndromes; Crohn's disease; CN_ELA2, cyclic neutropenia; ELA2, severe congenital neutropenia; FCAS, familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome; MWS, Muckle-Wells syndrome; NOMID, neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease; WAS, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; XLN, X-linked neutropenia. OS denotes Omenn syndrome where multiple disease genes were identified.
Roman numbers indicate 12 distinct disease clusters (DCs) of at least four PIDs about which at least five methods agreed.
| The colour coding for figure H | X |
| 0 | Not available |
| 1 | Combined immunodeficiencies (D81) |
| 2 | Immunodeficiency with predominantly antibody defects (D80) |
| 3 | Immunodeficiency associated with other major defects (D82) |
| 4 | Other immunodeficiencies (D84) |
| 5 | Functional disorders of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (D71) |
| 6 | Agranulocytosis (D70) |
| 7 | Albinism (E70.3) |
| 8 | Cerebellar ataxia with defective DNA repair (G11.3) |
| 9 | Constitutional aplastic anaemia (D61) |
| 10 | Crohn's disease [regional enteritis] (K50) |
| The colour coding for figure H | X |
| 0 | Not available |
| 1 | Combined immunodeficiency |
| 2 | Humoral immunodeficiency |
| 3 | Cellular immunodeficiency |
| 4 | Phagocytic cell disorders |
| 5 | Complement deficiencies |
| The colour coding for figure H | X |
| 0 | Not available |
| 1 | Predominantly T cell deficiencies, T-B- Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) |
| 2 | Predominantly antibody disorder |
| 3 | Other well definied PIDs |
| 4 | Complement deficiencies |
| 5 | Phagocytic disorders |
| 6 | Autoimmune and immunedysregulation syndromes |
| 7 | Autoinflammatory syndromes |
| The colour coding for figure H | X |
| 0 | Not available |
| 1 | Combined B and T cell immunodeficiencies |
| 2 | Deficiencies predominantly affecting antibody production |
| 3 | Defects in lymphocyte apoptosis |
| 4 | Other well-defined immunodeficiency syndromes |
| 5 | Defects of phagocyte function |
| 6 | Defects of innate immune system, receptors and signaling components |
| 7 | Periodic fever syndromes |
| 8 | Defects of the classical complement cascade proteins |
| 9 | Defects of the alternative complement pathway |
| 10 | Defects of complement regulatory proteins |
| 11 | DNA breakage associated syndromes and DNA epigenetic modification syndromes |